CC Aluminum Circle
CC aluminum circle refers to circular aluminum discs produced using the Continuous Casting and Rolling process (Continuous Casting and Rolling, abbreviated as CC or Cast Rolled). They are also commonly known as cast-rolled aluminum circles. Together with DC (Direct Chill, semi-continuous direct water-cooled casting) aluminum circles, they represent the two main product types in the aluminum circle market.
CC aluminum circles are widely used across many industries due to their cost-effective nature. If you are manufacturing aluminum circular components that do not require extremely high forming performance, CC aluminum circles are an ideal choice offering excellent value for money.
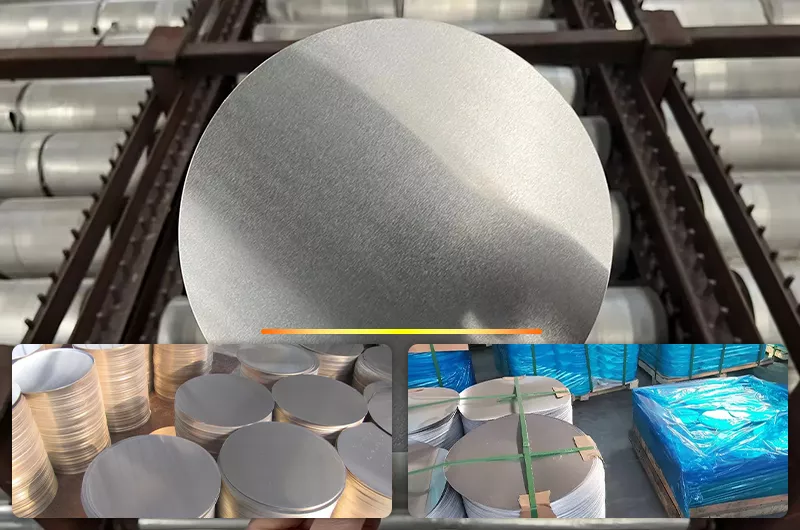
CC aluminum circles are an economical and efficient aluminum disc product manufactured through the continuous casting and rolling process. They are mainly used as forming raw materials for cookware, signage, lighting equipment, household appliances, and related products.
CC Aluminum Circle Technical Specifications
| Feature | Standard Specification |
| Common Alloys | 1050, 1060, 1100, 3003 |
| Temper | O (Soft), H12, H14, H16, H18 |
| Thickness Range | 0.2mm – 10mm |
| Diameter Range | 50mm – 1200mm |
| Surface Finish | Mill Finish, Bright, Anodized, or Pre-painted |
CC Aluminum Circle Alloys & Grades
Common alloy grades:
- 1xxx series: such as 1060, 1070, 1100 (pure aluminum series, offering excellent corrosion resistance, electrical and thermal conductivity, relatively low strength, and easy deep drawing).
- 3xxx series: such as 3003 (aluminum-manganese alloy, good anti-rust performance, higher strength than 1xxx series, commonly used for cookware and chemical containers).
- 5xxx series: such as 5052, 5083 (aluminum-magnesium alloys, excellent seawater corrosion resistance and high strength, commonly used in ships and vehicles).
CC Aluminum Circle Tempers & Grades
- H14: Half-hard temper, the most commonly used condition for cookware and lighting products, offering a balance of strength and formability.
- H18: Full-hard temper, high strength but relatively poor formability.
- O temper: Annealed temper, very soft, suitable for deep drawing applications, with subsequent heat treatment applied after forming to improve strength.
CC Aluminum Circle Features
- Production process: Molten aluminum is directly cast into a continuous strip, then cold rolled to the required thickness, and finally punched into circular shapes.
- Ductility: CC aluminum circles are well known for their excellent elongation and tensile strength, making them an ideal choice for spinning and drawing processes.
- Good surface quality: Smooth, fine, and uniform surface without obvious oxide scale or hot-rolling marks, making them highly suitable for subsequent anodizing, coating, polishing, and other surface treatments.
- High dimensional accuracy: Tight thickness tolerances and good concentricity, ideal for precision stamping and drawing.
- Excellent mechanical properties: Higher strength achieved through cold work hardening compared with hot-rolled or fully annealed materials.
- Good processing performance: Excellent ductility and formability, making them ideal materials for deep-drawn products such as cookware and lighting components.

Surface Treatment of CC Aluminum Circle
Common Surface Treatments: CC aluminum circles can be surface treated as needed, such as anodizing, coating, etc., to enhance their corrosion resistance and decorative properties.
CC aluminum circles are versatile and high-performance aluminum products, widely used in applications requiring lightweight, corrosion resistance, and good formability.
Haomei Aluminum CC aluminum circles feature high strength, formability, and excellent corrosion resistance and can be further processed through deep drawing, spinning, and other methods.
The Chemical Composition of different Alloy CC Aluminum Circle
| Alloy | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Ni | Zn | Ti | Zr | AL | |
| 1050 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 一 | — | 0.05 | 0.05V | 0.03 | — | 99.5 |
| 1060 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | — | 0.05 | 0.05V | 0.03 | — | 99.6 |
| 1070 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | — | — | 0.04 | 0.05V | 0.03 | — | 99.7 |
| 1100 | 0.95Si+Fe | 0.05~0.20 | 0.05 | — | — | — | 0.1 | i | — | — | 99 | |
| 3003 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.05~0.20 | 1.0~1.5 | — | — | — | 0.1 | — | — | — | remainder |
| 5052 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 2.2~2.8 | 0.15~0.35 | — | 0.1 | — | - | — | Remainder |
| 8011 | 0.50~0.9 | 0.6~1.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.05 | — | 0.1 | — | - | — | Remainder |
CC Aluminum Circle Applications
- Cookware and kitchenware: This is the most common application. Due to the excellent thermal conductivity of CC aluminum circles, they are widely used in frying pans, pressure cookers, stock pots, and non-stick cookware.
- Lighting industry: Owing to their high reflectivity and ease of spin forming, CC aluminum circles are used for high-bay lighting reflectors, recessed lighting, and lamp shades.
- Traffic signage: Used for road signs, traffic signs, and warning boards.
- Automotive components: Automotive lamp covers, filter housings, and decorative parts.
- Industrial components: Various stamped parts, gaskets, and electronic component housings.
- Electronics and electrical appliances: Capacitor housings, battery shells, small heat sinks, etc.
- Daily consumer goods: Bottle caps, easy-open ends, aluminum cans, cookware handles, and more.
- Architectural decoration: Ceiling decorative components, circular aluminum ceiling panels, and decorative hangings.

Advantages and Limitations of CC Aluminum Circles
Advantages of the CC Process
- Low cost: Fewer processing steps and lower energy consumption, saving approximately 30% energy compared with the DC process.
- High efficiency: Short production flow with strong continuity, suitable for large-scale production.
- Lower investment: Equipment investment is lower than that of the DC process, making it suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Limitations of the CC Process
- Coarse and non-uniform grain structure: Rapid solidification results in a microstructure that is not sufficiently dense.
- Relatively poor deep drawing performance: Elongation and formability are lower than those of DC aluminum circles.
- Average surface quality: Not as suitable as DC aluminum circles for fine surface treatments.
Comparison Between CC Aluminum Circles and DC Aluminum Circles
Although both are used for similar products, the choice depends on your specific manufacturing requirements:
- CC (Continuous Casting): Best suited for general-purpose cookware, offering lower cost and shorter production cycles. It is especially suitable for the "spinning" forming method.
- DC (Direct Chill Casting): More suitable for deep drawing applications (such as very deep pots or containers) and for high-end anodizing treatments that require perfectly uniform surfaces without any "orange peel" effect.
| Comparison Item | CC Aluminum Circle | DC Aluminum Circle | Applicable Scenario |
| Production process | Continuous casting and rolling | Direct chill semi-continuous casting + hot rolling + cold rolling | CC is suitable for large-volume, low-cost production, while DC is suitable for high-quality requirements |
| Grain structure | Coarse and non-uniform | Fine, dense, and uniform | DC is suitable for products requiring high strength and toughness |
| Deep drawing performance | Relatively poor (elongation approx. 20–25%) | Excellent (elongation approx. 30–40%) | DC is suitable for deep drawing products (such as pressure cookers and rice cooker inner pots) |
| Surface quality | Average | Excellent, suitable for fine finishing | DC is suitable for products requiring anodizing, coating, and other surface treatments |
| Price | Low (10–15% lower than DC) | Higher | CC is suitable for budget-sensitive, general applications; DC is suitable for high-end products |
| Typical applications | General cookware, signage, reflectors | Deep-drawn cookware, high-end appliance housings, precision parts | - |
- CC (Continuous Casting) circles are produced using a faster and more simplified manufacturing process with fewer steps, resulting in lower production costs.
- DC (Direct Chill) aluminum circles—manufactured through traditional direct chill casting and hot rolling processes—offer better surface finish and mechanical properties, and are generally more suitable for deep drawing and high-end cookware.
Parameters to Confirm Before Purchasing Haomei CC Aluminum Circles
As a professional aluminum circle manufacturer and supplier, Haomei Aluminum recommends that you clearly define the following key parameters before quotation and production planning, to ensure the products fully match your processing and application requirements:
Alloy Grade
Please confirm the required alloy type, such as 1060, 3003, 5052, etc. Different alloys vary in formability, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Material Temper
Specify the required temper, such as O (annealed), H14, H18, etc., to meet deep drawing, stamping, or finished product strength requirements.
Dimensional Specifications
Thickness: mm
Diameter: mm
We can customize production according to customer drawings or technical requirements to ensure dimensional accuracy and consistency.
Purchase Quantity
Please specify the required quantity (in pieces or tonnage) so that we can reasonably arrange production schedules and delivery times.
Surface Quality Requirements
Whether special surface finishes such as mirror, matte, or brushed are required, or whether there are specific control standards for oil stains, scratches, or oxidation spots.
At Haomei Aluminum, we provide aluminum circle products with stable dimensions, clean surfaces, and excellent forming performance through strict quality control and mature CC blanking processes. You are welcome to provide detailed parameters, and we will promptly develop a professional supply and technical solution for you.
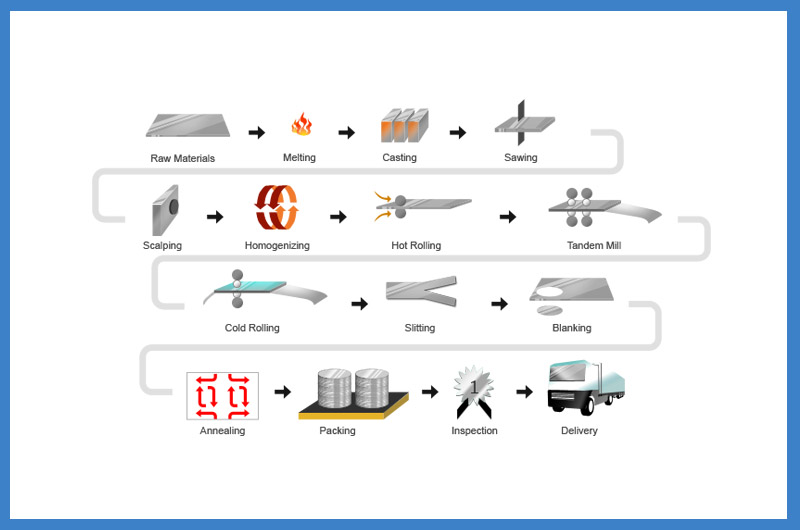
CC Aluminum Circle Production Process
The continuous casting (CC) process is an efficient and economical method for producing aluminum circles, particularly suitable for large-scale production.
Aluminum Liquid Casting
Aluminum Liquid Preparation: The aluminum liquid typically consists of aluminum blocks or alloys melted in an aluminum smelting furnace, refined and filtered to remove impurities, ensuring the purity and quality of the liquid aluminum.
Casting System: The aluminum liquid flows into a mold through the nozzle of the casting machine. The mold usually consists of two cooled metal plates that hold the aluminum liquid during casting. The aluminum liquid solidifies in the mold to form a preliminary aluminum strip.
Cold Rolling or Hot Rolling Processing
Cold Rolling: The preliminary cast aluminum strip is processed through a cold rolling mill, where multiple rollers compress the strip, reducing its thickness and improving its surface finish. Cold rolling occurs at room temperature and can further refine the thickness and properties of the aluminum strip.
Hot Rolling (if required): If specific thermal treatment properties are needed for the aluminum circles, the preliminary cast aluminum strip may undergo hot rolling. Hot rolling occurs at high temperatures, which helps improve the plasticity and flowability of the aluminum material, achieving the desired thickness.
Quality Control and Post-Processing
Quality Inspection: During the continuous casting process, aluminum circles undergo a series of quality checks, including thickness measurement, surface defect detection, and strength testing, to ensure the products meet specification requirements.
Cutting and Coiling: After rolling, the aluminum strip is cut into the required circle sizes or coiled for subsequent processing and use.
Deep drawing performance of cast aluminum circles is generally poorer compared to hot-rolled aluminum circles and is rarely used for deep drawing. High-quality aluminum circles are typically hot-rolled products, with no color difference after anodizing and strong ductility, suitable for stretching, deep drawing, spinning, anodizing, and other subsequent processes.