Deep Drawing Aluminum Circles
What Are Deep Drawing Aluminum Circles?
Deep drawing of aluminum circles is a specialized metal forming process used to transform flat aluminum circular blanks into hollow, cup-shaped parts. Due to aluminum’s light weight, corrosion resistance, and excellent ductility, it is one of the most commonly used materials for this process.
Deep Drawing Aluminum Circles are typically produced from aluminum alloy coils or sheets through precision slitting, blanking, or cutting. They feature accurate diameters and thicknesses and serve as the starting blanks for subsequent deep drawing forming operations.

Deep drawing is a metal forming technique that converts flat sheet or disc-shaped metal materials into hollow or complex-shaped objects—such as pots, pans, automotive components, or industrial containers—without causing material fracture or cracking.
Deep drawing aluminum circles are the critical link between high-quality aluminum materials and complex deep-drawn components. The core lies in the matching of “material” and “process”:
- Selecting the right material (high-ductility 1xxx and 3xxx series aluminum in O temper) is the foundation of success.
- Controlling quality (dimensional accuracy, surface cleanliness, and uniform mechanical properties) ensures stable mass production.
Features of Deep Drawing Aluminum Circles
- High formability: specifically manufactured to achieve large drawing depths without cracking.
- Uniform thickness: ensures consistent deformation during the deep drawing process.
- Customizable: available in various alloys (such as 1060, 3003, 5052), diameters, and thicknesses to meet different application needs.
- Corrosion resistance: maintains integrity even in harsh environments.
- Excellent deep drawing performance: the material must have high ductility, high elongation, and low yield strength to be stretched into deep shapes without rupture.
- Good surface quality: the surface should be smooth and clean, free from scratches, oxide scale, oil stains, or impurities, as these defects affect the surface quality of stamped parts and may damage tooling.
- Uniform mechanical properties: low anisotropy and consistent performance ensure uniform deformation during drawing and prevent “earing” (wavy protrusions at the rim).
- Precise dimensional tolerances: diameter and thickness must be strictly controlled to ensure smooth feeding and product consistency in high-speed automatic stamping.
Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Alloys & Grades
Not all aluminum alloys are suitable for deep drawing. The most commonly used grades belong to pure aluminum and soft aluminum-manganese/aluminum-magnesium alloys due to their excellent formability.
1xxx Series Pure Aluminum: such as 1100, 1050, 1060, 1070.
Characteristics: the higher the purity (e.g., 1070), the better the ductility, electrical and thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance, but with lower strength. It is one of the most commonly used materials for deep drawing.
3xxx Series Aluminum-Manganese Alloys: such as 3003, 3004, 3104.
Characteristics: manganese is added to pure aluminum, providing slightly higher strength than the 1xxx series while maintaining good formability and corrosion resistance. 3003 is widely used; 3004/3104, with higher strength, are commonly used for beverage can bodies.
5xxx Series Aluminum-Magnesium Alloys: such as 5052, 5083.
Characteristics: higher strength and excellent corrosion resistance (especially suitable for marine environments), with good formability, though slightly inferior to the 1xxx and 3xxx series. Used for deep-drawn parts requiring higher strength.
8xxx Series Aluminum Foil: such as 8011, 8021. Commonly used for very thin deep-drawn parts such as battery cases and capacitor housings.
Temper: O temper (annealed) is typically used, as it is the softest state with the best ductility, making it ideal for deep drawing.
Due to compositional differences, different aluminum alloy series exhibit varying deep drawing performance. Mainstream selections are as follows:
| Series | Typical Grades | Deep Drawing Performance | Main Applications |
| 1xxx Series (Pure Aluminum) | 1050, 1060, 1070, 1100 | Excellent, high ductility, low earing rate | Cookware, tableware, lighting products, general containers |
| 3xxx Series (Al-Mn Alloy) | 3003 | Good, better corrosion resistance than 1xxx series | Chemical containers, radiators, food packaging |
| 5xxx Series (Al-Mg Alloy) | 5052, 5083 | Good, higher strength | Pressure vessels, automotive parts, marine components |
| 8xxx Series (Al-Li / Al-Fe Alloy) | 8011 | Good, suitable for thin gauges | Bottle caps, easy-open ends, thin-wall containers |
Note: 1xxx series pure aluminum is the preferred choice for deep drawing aluminum circles due to its high purity, excellent ductility, and reasonable cost, meeting the majority of deep drawing requirements.
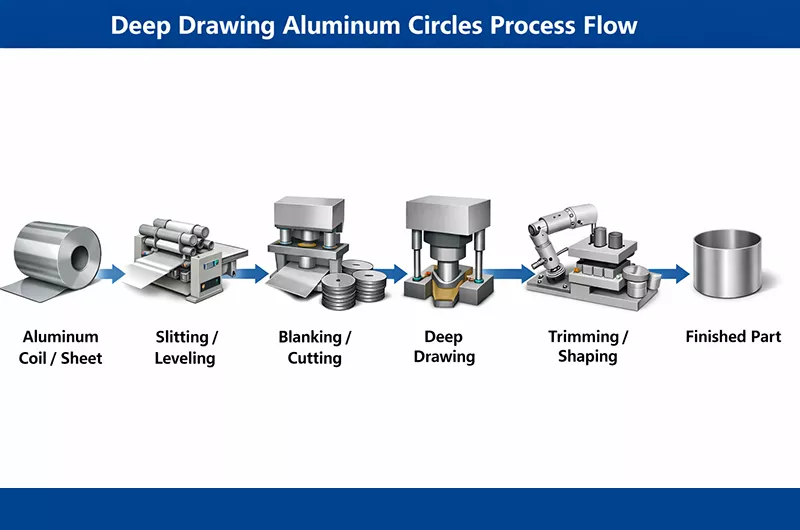
Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Process Flow
Brief description of the deep drawing process:
Aluminum coil/sheet → Slitting/Leveling → Blanking/Cutting (to obtain circular blanks) → Deep drawing (multiple drawing stages possible) → Trimming/Shaping → Finished parts
During the deep drawing process, a mechanical punch presses the aluminum circle into the die cavity. The final part’s “depth” is usually greater than its diameter.
- Blanking: cutting aluminum sheets into precise circular blanks.
- Clamping: the blank is held in place by a blank holder to prevent wrinkling.
- Drawing: the punch presses the center of the blank into the die, causing plastic flow of the metal and forming the container wall.
- Ejection: removing the finished part from the die.
Advantages of Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Discs
- High Precision: Deep drawing allows precise control over the final product's dimensions and shape.
- Surface Quality: The process produces a smooth surface finish, which is important for both aesthetic and functional purposes.
- Material Efficiency: The deep drawing process is efficient in material usage, reducing waste compared to other forming methods.
- It is about one-third the weight of steel, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring a certain strength-to-weight ratio.
- It has good dent resistance for automotive exterior panels.
- It is fully recyclable.
- It has rust-resistant properties (brown rust).
Limitations of Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Discs
- It is significantly more expensive than steel.
- It is abrasive to tools (aluminum oxide is very abrasive).
- Welding is difficult.
- It is prone to severe springback.
What is the Best Aluminum for Deep Drawing?
Common alloys for deep drawing include 1060, 3003, and 5052, and the temper greatly affects the deep drawing performance of aluminum circles. It is well-known that aluminum circles require annealing during processing to achieve different softness and hardness levels.
As the annealing time changes, the stretchability and elongation of the aluminum sheet also vary. In other words, the longer the annealing time, the more suitable the aluminum alloy is for the deep drawing process. Aluminum sheets in the O temper are best suited for deep drawing.
The choice of 1060, 3003, and 5052 alloys is based on their excellent deep drawing properties, including good formability and surface finish. 1050, 1060, 1070, and 1100 aluminum discs hot-rolled for deep drawing are suitable for cookware.
Thickness: The thickness of aluminum circles can vary, typically between 0.5 mm to 5 mm, depending on the application and requirements.
Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Disc 1060
- Available Tempers: O, H22, H24
- Deep Drawing Suitability: 1060 aluminum is very suitable for deep drawing processes, especially in the O temper. This temper provides the best formability, allowing for deeper and more complex drawing operations without compromising the material's integrity. For applications requiring minimal stretch depth or a certain hardness, H22 or H24 tempers can be used. These tempers offer higher hardness while still maintaining good drawability.
- Applications: Ideal for cookware, automotive parts, and decorative items requiring excellent formability and surface finish.
Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Disc 3003
- Deep Drawing Suitability: 3003 aluminum is typically used for applications with lower stamping requirements. It is suitable for cases where a certain hardness needs to be maintained. The O temper of 3003 aluminum compensates for the lower hardness of the 3xxx series alloys, making it suitable for deep drawing while achieving a reasonable balance between formability and hardness.
- Applications: Commonly used for manufacturing parts requiring moderate formability and durability, such as household products, kitchen utensils, and some light industrial components.
Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Disc 5052
- Suitability for Deep Drawing: 5052 aluminum alloy is renowned for its excellent deep drawing performance. It is typically used for applications requiring substantial stretching without material failure. However, due to the nature of the alloy, the disc may not become excessively hard after drawing, as overly high hardness may lead to cracking or splitting. The final performance depends on the drawing height and method, which should be carefully managed to achieve the desired performance without damaging the material.
- Applications: Commonly used for high-strength applications, such as marine environments, automotive parts, and high-pressure applications where both strength and formability are critical.
Applications of Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Discs
- Cookware: pots, frying pans, pressure cookers, woks, soup pots, and rice cooker inner pots.
- Beverage cans: soda and beer cans are the highest-volume deep-drawn products.
- Automotive: fuel tank components, heat shields, filter housings, and lighting parts.
- Electronics: capacitor housings and shielding covers.
- Packaging industry: food cans, beverage cans, easy-open ends, bottle caps.
- Lighting industry: lampshades, reflectors, LED heat sinks, reflective components, lamp bodies.
- Chemical industry: pressure vessels, dished heads, liquid storage tanks.
- Others: aluminum crafts, medical device components, aerospace parts.

Deep-drawn aluminum circles are used in cookware.
- Pots and Pans: Deep-drawn aluminum circles are used to manufacture various types of cookware, including frying pans, stewpots, and soup pots. The process creates a uniform, smooth surface, ensuring even heat distribution.
- Pressure Cookers: The deep drawing process is used to produce the body of pressure cookers, providing necessary strength and durability while maintaining a lightweight characteristic.
Deep-drawn aluminum circles are used in lighting fixtures.
- Lamp Shades: Aluminum circles are deep-drawn to form the basic structure of lamp shades, then finished with various coatings and textures.
- Reflectors and Housings: These components benefit from the deep drawing process, as it achieves precise forming and smooth surface treatment, which is crucial for optimal light reflection and aesthetics.
Deep-drawn aluminum circles are used in automotive parts.
- Engine Components: Deep-drawn aluminum circles are used to produce certain engine parts that require lightweight and strength.
- Body Panels: Aluminum circles are used to manufacture body components, such as panels and decorative elements.
Deep-drawn aluminum circles are used in ventilation systems.
Circular Duct Components: Deep drawing is used to produce circular components for ventilation systems, including ducts and housings, ensuring a robust and streamlined design.
Chemical compositon of different alloy deep drawing aluminium circle
| Grade | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Ni | Zn | Al |
| 1060 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | - | - | 0.05 | 99.6 |
| 3003 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.05-0.2 | 1.0-1.5 | - | - | - | 0.1 | remains |
Key Considerations for Deep Drawing Aluminum Materials
Aluminum behaves differently from steel during drawing. The following are key factors to ensure successful deep drawing:
Alloy Selection
Not all aluminum is the same. The temper (hardness) and alloy type determine how far the metal can be drawn without tearing.
- 1xxx series (e.g., 1050, 1100): excellent formability; used for simple kitchenware.
- 3xxx series (e.g., 3003): the “workhorse” of deep drawing, offering a balance of strength and high ductility.
- 5xxx series (e.g., 5052): higher strength, commonly used for structural or marine applications.
Key Considerations for Deep Drawing Aluminum Materials
Drawing Ratio
The drawing ratio is an important parameter to evaluate deep drawing difficulty and material formability, typically defined as:
Drawing Ratio = Blank Diameter ÷ Punch Diameter
A higher drawing ratio means greater deformation during deep drawing and places higher demands on aluminum elongation, ductility, and grain structure.
For aluminum, a single drawing ratio is usually kept within 1.8–2.2 for safety.
If the drawing ratio is too large, the following defects may occur:
- Cracking or tearing
- Wrinkling
- Uneven wall thickness
Optimization recommendations:
- Select high-ductility aluminum alloys (such as 1060, 1070, 3003).
- Use multi-stage deep drawing to gradually reduce deformation.
- Improve material ductility through intermediate annealing.
Lubrication
Aluminum tends to gall or adhere to tooling. High-quality lubricants are essential to reduce friction and ensure smooth surfaces.
Main functions of lubrication:
- Reduce the friction coefficient between aluminum and the die.
- Minimize scoring, scratches, and surface tearing.
- Extend die service life.
- Help increase the allowable drawing ratio.
Common lubrication methods:
- Dedicated deep drawing oils
- Graphite-based or grease-type lubricants
- Water-soluble lubricants (suitable for applications requiring subsequent cleaning or food-grade use)
Key points for lubricant selection:
- Choose appropriate viscosity based on aluminum alloy type and drawing depth.
- For cookware and food containers, use non-toxic, easy-to-clean lubricants.
- Ensure uniform lubricant application to avoid localized dry friction.
Grain Direction
“Earing” occurs when wavy edges appear on the rim of the cup. This is caused by differences in aluminum properties due to grain direction formed during rolling. High-quality circular blanks are typically processed to minimize this anisotropy.

Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Quality Standards
Diameter tolerance: typically ±0.1 mm
Thickness uniformity: deviation < ±5%
Surface finish: free from scratches, dents, oxidation, or oil residues
Mechanical properties: high elongation (≥25%), suitable for forming
Deep Drawing Aluminum Circle Selection & Purchasing Considerations
Selection Guide
- Choose material based on application: 1060 for general cookware; 3003 for corrosion resistance; 5052 for higher strength requirements.
- Confirm temper: O temper or H0 ultra-soft condition is required; avoid hard tempers such as H18.
- Evaluate production process: hot-rolled base material is preferred, especially for high surface quality requirements.
- Verify quality indicators: focus on grain size, earing rate, and surface quality.
- Customization capability: select suppliers that can meet requirements for size, thickness, and surface treatment.
When purchasing or customizing deep drawing aluminum circles, the following parameters should be clearly defined:
Alloy grade and temper: select appropriate grades (such as 1060-O, 3003-O) based on final strength, corrosion resistance, and subsequent processing (e.g., anodizing).
Dimensional Specifications:
Diameter: accurate to the millimeter, typically with ±0.1 mm or tighter tolerances.
Thickness: critical, with strict tolerance requirements (e.g., ±0.02 mm).
Surface Treatment: is pre-oiling (drawing oil) required for stamping? Should the surface be bright, matte, or PTFE-coated?
Mechanical Property Requirements: for critical structural parts, suppliers may be required to provide tensile test data (yield strength, elongation, etc.).
Packaging & Transportation: to prevent scratches, interleaving paper, stacked packing, or dedicated pallets are commonly used.
Why Choose Haomei Aluminum for Deep Drawing Aluminum Circles
Haomei Aluminum specializes in the R&D and manufacturing of high-quality deep drawing aluminum circles. Using high-purity aluminum materials combined with precision cutting and strict quality control, we ensure smooth, defect-free surfaces and stable, controllable thickness and diameter tolerances, significantly improving forming consistency and yield rates during deep drawing.
Our aluminum circles feature high elongation and excellent ductility, effectively reducing risks of cracking and wrinkling and making them suitable for multi-stage deep drawing processes. Haomei Aluminum offers both standard specifications with ready stock and fully customized solutions for diameter, thickness, alloy, and temper, enabling rapid response to diverse customer production needs. We are your reliable partner for deep drawing manufacturing.
What is the difference between deep drawing and stamping?
The difference between deep drawing and stamping is that deep drawing is primarily used for creating complex-shaped deep parts, while stamping is used for efficiently manufacturing various thin sheet metal parts.
Deep Drawing and Stamping are two common metal processing techniques. Although both involve shaping metal materials, their processes and applications differ.
Deep Drawing
- Process: Deep drawing is a process used to stretch metal sheets into complex shapes. Typically, the metal sheet is placed in a die, and a punch pushes the sheet downward into the die to form a deep container shape. This process requires significant pressure to stretch the metal into the desired shape.
- Applications: Deep drawing is commonly used to manufacture various deep parts, such as cookware, automotive fuel tanks, and appliance housings. This process is particularly suitable for producing parts with complex and deep shapes.
- Materials: Generally uses thinner metal sheets, such as aluminum or steel plates.
- Characteristics: Capable of handling more complex shapes but requires higher material ductility and precise process control.
Stamping
- Process: Stamping is a process that involves cutting, forming, or embossing metal sheets through dies. Stamping usually includes multiple steps, such as cutting, bending, and punching. The process deforms the metal plastically through the pressure applied by the dies.
- Applications: Stamping is widely used to produce various metal parts, such as automotive parts, appliance components, and construction materials. Stamping is typically used for large-volume production of relatively simple parts and is suitable for manufacturing thin sheet parts.
- Materials: Can use metal sheets of various thicknesses, including steel and aluminum.
- Characteristics: Suitable for efficient, high-volume production, capable of manufacturing relatively simple parts but with certain limitations on material thickness and complexity.
