Aluminum fins are essentially extended surface heat exchange elements. Their working principle is based on the synergistic effect of thermal conduction and convective heat transfer. When the heat medium flows inside the base tube, heat is conducted through the tube wall to the aluminum fins, which then rapidly dissipate the heat into the surrounding air, achieving efficient cooling.
The core function of aluminum fins is to increase the heat dissipation area and improve heat exchange efficiency, thereby addressing the bottleneck problem of "insufficient surface area" in traditional plain tubes.

Aluminum fin stock is mainly used in heat exchangers and heat transfer applications. It is commonly found in automotive radiators, condensers, and various HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) components. This material is typically made from 1000, 3000, and 8000 series aluminum alloys and is supplied in coil or foil form.
Role of Aluminum Fins in Heat Dissipation
| Functional Role | Description | Practical Effect |
| Expand Heat Dissipation Surface Area | Through dense fin arrays (e.g., louvered/wavy designs), the surface area increases 10 to 100 times compared to the base | Significantly increases contact area with air, accelerating convective heat exchange |
| Establish Effective Thermal Conduction Path | Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity (237 W/m·K) rapidly transfers heat from the source (e.g., copper tubes/chips) to the fin tips | Lowers local temperature at the heat source, avoiding overheating damage |
| Enhance Air Convective Heat Transfer | Fin spacing forms air channels that enable forced airflow (fans) or natural convection to carry heat away | Improves heat dissipation rate by 3–8 times compared to flat surfaces without fins |
| Lightweight Structural Support | Aluminum’s low density (2.7 g/cm³) ensures strength while reducing overall weight | Suitable for weight-sensitive applications such as automobiles |
Common Aluminum Alloys for Fins
- 1000 Series Pure Aluminum contains more than 99.0% aluminum. It has excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance, with outstanding workability but relatively low strength.
- 3000 Series Aluminum-Manganese Alloys offer medium strength, good corrosion resistance, weldability, and formability, making them a common choice for fin materials.
- 8000 Series Aluminum Alloys have good formability and medium strength, making them commonly used for fin materials, especially in air conditioning and heat exchange applications.
- 4000 Series Aluminum-Silicon Alloys feature lower melting points and good brazing performance, often used as cladding materials for brazing applications.
3000 Series Aluminum-Manganese Alloy Fin Stock
Represented by 3003 and 3004, with manganese as the main alloying element, they offer medium strength, good corrosion resistance, weldability, and formability. 3003 aluminum alloy is a common choice for fin materials due to its good forming properties and corrosion resistance, suitable for applications requiring higher strength than 1000 series alloys. 3004 alloy has higher strength than 3003 and is especially suitable for fin applications demanding greater strength.
8000 Series Aluminum Alloy Fin Stock
Represented by 8011, an aluminum-silicon alloy with good formability and medium strength, it is a commonly used choice for fin materials, particularly in air conditioning and heat exchange applications. 8006 aluminum alloy performs excellently in UV resistance, maintaining a high gloss retention rate even after 1000 hours of UV testing.
4000 Series Aluminum-Silicon Alloy Fin Stock
Represented by 4343, 4045, 4047, etc., with silicon as the main alloying element, they have lower melting points and excellent brazing properties. 4343 aluminum alloy is a commonly used cladding material for brazing. When combined with 3003 core material, it forms composite fin aluminum foil, widely used in automotive heat exchangers.
Alloy Selection Guide for Different Application Scenarios
- Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Systems usually adopt 1100, 3003, and 8011 alloys. These materials have good thermal conductivity and formability, meeting the requirements for heat dissipation efficiency and processability in air conditioner fins. Hydrophilic aluminum fin foils require special coating treatments on the base alloy to enhance surface hydrophilicity and corrosion resistance.
- Automotive Radiators commonly use 3003/4343 composite aluminum foil. This material has excellent brazing properties and anti-sag performance. In automotive heat exchangers, composite fin aluminum foil is widely used due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity.
- Industrial Heat Exchangers require alloy selection based on medium characteristics and operating conditions. For general industrial environments, 3003 and 3004 alloys are commonly chosen.
Specifications of Aluminum Fins
Main dimensional parameters and tolerance standards for aluminum fins
The specification parameters of aluminum fins directly affect their heat dissipation performance and installation compatibility. Understanding these parameters and tolerance standards is crucial for proper selection and use of aluminum fins.
- Thickness: usually between 0.1–0.3mm, with tolerance controlled within ±0.05mm
- Width: commonly ranges from 100–450mm, up to a maximum of 2650mm, tolerance within ±1mm
- Fin Height: typically ranges from 4–12mm, with a tolerance of ±0.5mm
- Fin Pitch: usually between 1.5–8.0mm, tolerance ±0.1mm
- Fin Angle: typically controlled within -1 to +1 degree
Haomei Aluminium Fin Stock Manufacturing and Supply
| Units | Thickness | Width (Diam.) | Coil Internal Diameter | Coil External Diameter | Coil Weight | Alloys | |||||
| min | max | min | max | min | max | min | max | min | max | ||
| Inches | 0.0039 | 0.0100 | 1 | 47 | 3 | 6 | - | 24 | - | 925 Lb | 1XXX, 3XXX, 8XXX |
| mm | 0.1 | 0.254 | 25.4 | 1, 200 | 76 | 152 | - | 600 | - | 420 kg | |
- Alloy: Commonly used alloys include the 1000 series (industrial pure aluminum), 3000 series (aluminum-manganese alloys), and 8000 series (aluminum-zinc alloys).
- Form: Fin stock is typically produced in coil or foil form with specific thickness ranges and temper conditions.
- Cladding: Some fin stocks may be clad with different alloys, such as cladding 4004 alloy onto a 3003 core material, to suit specific applications like vacuum brazing.
Surface and Appearance of Haomei Fin Material Aluminum Foil
- Clean, free of fishtail marks, folds, scratches, or other defects.
- No adhesion or discoloration on the surface.
- Edges are flat, smooth, and crack-free.
- No noticeable color difference between coils or between layers of a single coil.
Performance Advantages of Aluminum Fins
Thermophysical Properties of Aluminum Fins
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum has a thermal conductivity of up to 237W/(m·K), much higher than many other metals. This allows aluminum fins to quickly absorb and transfer heat, improving heat exchange efficiency. While aluminum's thermal conductivity is lower than copper's, its low density, cost-effectiveness, and good corrosion resistance make it the preferred choice for fin materials.
- Heat Capacity: The specific heat capacity of aluminum is approximately 900J/(kg·K), which means aluminum fins can absorb or release a large amount of heat during temperature changes, helping to stabilize thermal fluctuations. This makes aluminum particularly suitable for heat exchange applications requiring quick thermal response.
- Thermal Expansion Coefficient: Aluminum has a thermal expansion coefficient of about 23.6×10^-6/°C, which is relatively high. When designing aluminum fin systems, it is important to consider the expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes to avoid excessive stress or deformation.
- Thermal Radiation Characteristics: Aluminum surfaces have good thermal radiation properties, especially when specially treated. Anodizing or coating can further enhance the radiation performance of aluminum fins and improve their efficiency in radiative heat exchange.
- Fin Efficiency: Fin efficiency refers to the ratio of the actual heat dissipation of the fin to the ideal heat dissipation assuming the entire fin is at the base tube temperature. The efficiency of aluminum fins typically ranges from 70% to 95%, depending on the fin geometry, thermal conductivity of the material, and operating conditions. Higher efficiency means better heat dissipation per unit of material.
Mechanical Properties and Durability of Aluminum Fins
- Strength and Hardness: The strength of different aluminum alloys varies widely, ranging from about 70 MPa for pure aluminum to over 300 MPa for high-strength alloys. In terms of hardness, aluminum fins are commonly produced in tempers such as H14, H18, and H24 to meet various application requirements.
- Toughness and Ductility: Aluminum fin materials need to have sufficient toughness and ductility to withstand deformation during processing and vibrations during use.
- Anti-Sag Performance: During high-temperature brazing, aluminum fins must have good anti-sag properties to prevent deformation due to gravity. Optimizing alloy composition and heat treatment processes can significantly enhance this capability.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum naturally forms a dense aluminum oxide film in air, providing excellent corrosion resistance. The level of corrosion resistance varies slightly among different alloys. Additionally, surface treatments such as anodizing and coating can further improve the corrosion resistance of aluminum fins.
- Vibration Resistance: In vibrating environments, aluminum fins must exhibit good resistance to fatigue and fracture. Bimetallic steel-aluminum clad fins offer notable advantages in this regard, combining the high strength of steel and excellent thermal conductivity of aluminum to effectively withstand mechanical vibrations.
Fluid Dynamic Characteristics of Aluminum Fins
- Airflow Resistance: Airflow across aluminum fins generates resistance, which is affected by the fin shape, pitch, and height. Generally, smaller pitch and taller fins result in higher airflow resistance. Fin design must balance surface area and resistance to optimize heat exchange efficiency and energy consumption.
- Boundary Layer Effect: A thin boundary layer of air forms on the fin surface, which hinders heat transfer. Optimizing fin shapes can disrupt this layer and increase the heat transfer coefficient.
- Turbulence Promotion: Special fin designs can enhance air turbulence and improve heat transfer efficiency. For example, corrugated fins create periodic flow disturbances to increase turbulence, while spiral fins guide air into a helical flow pattern, extending contact time between air and fins.
- Pressure Drop Characteristics: Airflow through aluminum fins results in a pressure drop, directly affecting fan or pump energy consumption. It is essential to control this pressure drop within reasonable limits to ensure system efficiency. Typically, larger pitch and smoother surfaces result in lower pressure drops.
- Frosting and Condensation Behavior: In low-temperature or high-humidity environments, aluminum fin surfaces may experience frosting or condensation, reducing heat exchange efficiency. Hydrophilic aluminum fin foils use special surface treatments to improve wettability, reduce condensation and frosting, and enhance performance in humid conditions.
Influence of Material on Aluminum Fin Performance
| Performance Indicator | 1000 Series (1100, 1200) | 3000 Series (3003, 3102) | 8000 Series (8011, 8079) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent, high purity aluminum with superior thermal efficiency | Good, slightly lower than 1000 series but still meets heat exchange requirements | Moderate to low, suitable for general heat exchange applications |
| Strength | Low, limited mechanical load-bearing capacity | Moderate to high, good structural strength | Moderate to high, suitable for applications requiring post-forming strength |
| Formability | Excellent, highly ductile, suitable for deep drawing | Good, suitable for regular stamping and rolling processes | Excellent, especially suitable for complex and ultra-thin structures |
| Corrosion Resistance | Outstanding, suitable for neutral or mildly corrosive environments | Excellent, adaptable to humid or mildly acidic/alkaline environments | Good, with stable oxidation and corrosion resistance |
| Suitable Applications | Scenarios requiring high thermal conductivity, such as high-end heat exchangers | General-purpose fins, suitable for air conditioners, automobiles, etc. | Deep-drawing and thin-structure applications, such as hydrophilic fins and energy-saving designs |
Classification of Aluminum Fin Stock
Classified by Alloy Composition
- Pure aluminum fin stock (1000 series)
- Aluminum-manganese alloy fin stock (3000 series)
- Aluminum-magnesium alloy fin stock (8000 series)
- Aluminum-silicon alloy fin stock (4000 series)
Classified by Structural Form
- Clad aluminum fin stock
- Non-clad aluminum fin stock
- Single-metal fin stock
- Bimetal composite fin stock
Classified by Surface Treatment
- Bare/Non-coated Aluminum Fin
- Pre-coated Aluminum Fin
- Hydrophilic Aluminum Fin
- Hydrophobic Aluminum Fin
- Anti-mold Aluminum Fin
- Color-coated Aluminum Fin
- Clad aluminum fin stock: A layer or two of different aluminum alloys is clad onto the surface of the core aluminum alloy, such as the composite structure 4343/3003/4343 aluminum foil, mainly used in brazed heat exchangers.
- Non-clad aluminum fin stock: Fin stock made from a single aluminum alloy without cladding, suitable for applications that do not require brazing or special surface treatment.
- Single-metal fin stock: The fin and the base tube are made from the same material, usually aluminum alloy, offering good thermal conductivity and consistency.
- Bimetal composite fin stock: The fin and base tube are made from different materials, such as an aluminum fin clad onto a steel base tube, combining the high strength of steel with the excellent thermal conductivity of aluminum.
Characteristics and Features of Aluminium Fin Stock
High Thermal Conductivity
High thermal conductivity (approx. 237 W/m·K), about 50% faster than stainless steel.
Key to achieving rapid cooling/heating cycles, significantly improves heat exchanger (e.g., radiator, HVAC, automotive systems) efficiency.
Lightweight
Low density, reduces system weight by 30–50% compared to copper.
Advantages: Improves vehicle fuel efficiency, simplifies HVAC installation processes.
Corrosion Resistance
Naturally forms a dense oxide film to resist atmospheric corrosion, saltwater, moisture, and chemical attack. Optional coatings (such as hydrophilic coatings, epoxy coatings) enhance protection, suitable for humid/harsh industrial environments.
Formability and Manufacturing Flexibility
Easily stamped into complex fin structures (such as louvered or wavy shapes) without cracking.
Blank Processing: Aluminum foil is rolled into ultra-thin and uniform sheets, ensuring precise forming of complex corrugated structures.
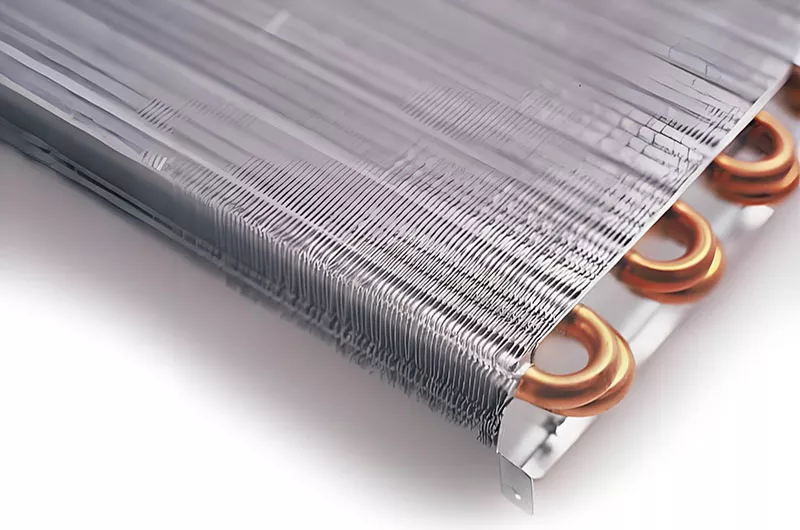
Common Fin Stock alloys and tempers include
- 1100 O Aluminum Fin Stock: Soft annealed condition for general formability.
- 1100 H14 Aluminum Fin Stock: Slightly strain-hardened, suitable for moderate strength and formability.
- 1100 H18 Aluminum Fin Stock: Higher strength than H14 due to further strain hardening.
- 1100 H19 Aluminum Fin Stock: Similar to H18 but with higher strength characteristics.
- 1100 H25 Aluminum Fin Stock: Strain-hardened to achieve increased strength.
- 1100 H111 Aluminum Fin Stock: Fully annealed to achieve maximum ductility.
- 1100 H211 Aluminum Fin Stock: Strain-hardened and partially annealed for improved strength and formability.
- 1100 H113 Aluminum Fin Stock: Strain-hardened and partially annealed with a controlled amount of cold work.
- 3003 O Aluminum Fin Stock: Soft annealed condition for good formability and corrosion resistance.
- 3003 H14 Aluminum Fin Stock: Strain-hardened, suitable for moderate strength and formability.
- 3003 H18 Aluminum Fin Stock: Higher strength than H14 due to further strain hardening.
- 3003 H19 Aluminum Fin Stock: Similar to H18 but with higher strength characteristics.
- 3003 H25 Aluminum Fin Stock: Strain-hardened to achieve increased strength.
- 3003 H111 Aluminum Fin Stock: Fully annealed to achieve maximum ductility.
- 3003 H211 Aluminum Fin Stock: Strain-hardened and partially annealed for improved strength and formability.
- 3003 H113 Aluminum Fin Stock: Strain-hardened and partially annealed with a controlled amount of cold work.
These aluminum fin stocks, ranging from annealed (O) to fully hardened (H113) tempers in both 1100 and 3003 alloys, are commonly used in heat exchangers and HVAC components such as air conditioners, radiators, and evaporators.
Chemical Composition of Different Alloy Aluminum Fin Stock
| Chemical composition of Aluminium fin stock Alloy (%) | AA1050 | AA1100 | AA1200 | AA3003 | AA8006 | AA8011 |
| Fe | 0.40 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 1.40 — 1.60 | 0.6 — 1.00 |
| Si | 0.25 | (Fe Si) | (Fe Si) | 0.60 | 0.02 | 0.5 — 0.90 |
| Mg | 0.05 | – | – | – | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Mn | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 1.0 — 1.50 | 0.4 — 0.50 | 0.20 |
| Cu | 0.05 | 0.05 — 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.05 — 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| Zn | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| Ti | 0.03 | – | 0.05 | 0.1(Ti Zr) | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| Cr | – | – | – | – | – | 0.05 |
| Each(Others) | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Total (Others) | – | 0.15 | 0.125 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Al | 99.50 | 99.00 | 99.00 | Remainder | Remainder | Remainder |
Applications of Aluminium Fin Stock
- HVAC and Refrigeration Field Widely used in various HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) equipment and refrigeration devices, it serves as the core material for aluminum radiators, evaporators, and condensers. Specific applications include household air conditioners, refrigerators, specialized refrigeration equipment, and automotive air conditioning systems, enhancing heat exchange efficiency to achieve cooling or heating functions.
- Transportation Sector Plays a crucial role in automobiles, railway vehicles, ships, airplanes, and other means of transportation. It is the primary manufacturing material for automotive radiator fins, ensuring efficient heat dissipation. Additionally, in various heat dissipation systems of other transport vehicles, its lightweight advantage allows it to effectively meet cooling requirements in space-constrained environments.
- Industrial Cooling and Heat Exchange Sector Suitable for industrial heat exchange scenarios, including heat exchangers in industrial processes or cooling systems, as well as heat dissipation in motors and transformers, hydraulic system cooling, compressor cooling, and other industrial equipment cooling scenarios. By increasing the surface area, it significantly improves heat dissipation efficiency.
- Construction and Decoration Sector In architectural applications, it can serve as a building shading element or facade decorative component. At the same time, it functions as an air heat exchanger in ventilation systems, enhancing the building’s appearance, improving ventilation efficiency, and reducing energy consumption.
- Home Appliances and Electronics Field Acts as a heat sink in home appliances and electronic devices, helping to dissipate the heat generated during the operation of electronic components, ensuring stable device performance and extending service life.
- New Energy Sector Applied in solar water heaters, solar collectors, fuel cells, and other new energy equipment. By participating in the heat exchange process, it improves energy conversion efficiency and supports the efficient utilization of new energy sources.
In addition, aluminum fin stock can also be embedded into thermal insulation shields, playing a role in temperature regulation and protection of sensitive components, further expanding its range of applications.
| Application Field | Description |
| Air Conditioning and Refrigeration | Aluminum fin stock is widely used in condensers and evaporators of air conditioning and refrigeration systems. Its high thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat exchange between the refrigerant and air, improving the system’s Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER). Moreover, the lightweight nature of aluminum helps reduce the overall equipment weight, facilitating installation and maintenance. Additionally, aluminum fins with corrosion-resistant coatings can effectively extend the service life of equipment, particularly in high-humidity environments such as household air conditioners, commercial refrigeration systems, and industrial cold storage. |
| Automotive Industry | Aluminum fin stock is primarily used in radiators, intercoolers, and condensers in the automotive industry. These components rely on aluminum fins’ large surface area and excellent thermal conductivity to achieve efficient heat transfer, ensuring the stable operation of engines, turbocharging systems, and air conditioning systems. The use of aluminum fins effectively enhances fuel efficiency, reduces the risk of engine overheating, and contributes to vehicle lightweighting trends, further improving energy efficiency and environmental performance. |
| Building Heating | Aluminum fin stock is widely used in building heating systems, including radiators and fan heaters. Its excellent thermal conductivity allows rapid heat transfer, ensuring uniform indoor temperature increases and improving heating efficiency. Additionally, aluminum alloy fins offer strong oxidation and corrosion resistance, making them less prone to rust or failure during long-term use. For rooftop or exterior wall heat dissipation systems, aluminum fins can be treated with colored coatings, such as gold or blue, to enhance the building’s aesthetics while improving UV resistance and weather durability. |
| Industrial Heat Exchange | Aluminum fin stock plays a crucial role in heat exchange equipment in the petrochemical and power industries, such as high-temperature gas coolers and heat recovery systems in chemical reactors. Due to aluminum’s excellent thermal conductivity and oxidation resistance, it maintains stable heat dissipation performance in high-temperature, high-humidity, and corrosive environments, ensuring long-term operational efficiency of heat exchange systems. Moreover, aluminum fins are lightweight and easy to process, allowing for customized designs based on different equipment requirements, improving heat exchange efficiency, and reducing maintenance costs. |
| Drying and Heating | Aluminum fin stock is widely used in drying equipment for the food and pharmaceutical industries, such as spray drying systems, to accelerate moisture evaporation and improve drying efficiency. Its high thermal conductivity allows heat to be quickly transferred to drying air or steam, thereby enhancing production speed and reducing energy consumption. At the same time, aluminum’s corrosion resistance ensures that fins maintain stable performance in high-temperature, humid environments, making them particularly suitable for food and pharmaceutical industries that require high hygiene and product quality standards. |
8011 O Aluminium Fin Stock for Air Conditioning
8011 O-grade aluminum foil is used for heat exchangers in air conditioning systems. It is made from 8011 aluminum alloy with O-temper (softened) treatment, making it suitable for air conditioning heat exchangers with good thermal conductivity.
Features:
- Material: 8011 aluminum alloy, O-temper (softened), suitable for processing.
- Application: Mainly used in heat exchangers within air conditioning systems.
- Performance: Provides good thermal conductivity and durability.
3003 Pre-coated Hydrophilic Aluminum Fin Stock for Heat Exchanger
3003 Pre-coated Hydrophilic Aluminum Fin Stock features a hydrophilic coating that enhances heat exchange efficiency by reducing water droplet formation and improving heat dissipation.
Features:
- Material: 3003 aluminum alloy with pre-coated hydrophilic layer.
- Hydrophilicity: The coating allows condensed water to spread rapidly, reducing water droplet formation.
- Application: Primarily used in various heat exchangers to enhance heat exchange efficiency.
8011 Pre-Coated Gold Color Aluminum Fin Stock for HVAC Heat Exchangers
8011 Pre-coated Gold Color Aluminum Fin Stock features a gold-colored coating that provides an attractive appearance while enhancing the protective properties of the aluminum foil, making it suitable for HVAC systems.
- Material: 8011 aluminum alloy with pre-coated gold protective layer.
- Appearance: The gold coating provides an aesthetically pleasing look and additional protection.
- Application: Suitable for heat exchangers in HVAC systems, combining aesthetics with functionality.
8011 O Blue Pre-coated Hydrophilic Aluminium Fin Stock for Household Air Conditioner
8011 O-grade aluminum foil with a blue pre-coated hydrophilic layer ensures rapid dispersion of condensed water. The blue coating adds visual appeal and enhances heat exchange efficiency.
- Material: 8011 aluminum alloy, O-temper (softened), with pre-coated blue hydrophilic layer.
- Hydrophilicity: The coating allows condensed water to spread rapidly, preventing water droplet formation.
- Appearance: The blue coating provides additional visual effects.
- Application: Designed specifically for household air conditioning systems, improving both heat exchange efficiency and appearance.
The Main Experimental Test of Haomei Aluminum Fin Stock
The quality of aluminum fin material directly affects the performance and reliability of the heat exchange system. Therefore, strict quality control standards are required, covering chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, surface quality, metallographic structure, and physical properties.
- Chemical Composition Analysis Common methods include spectroscopic analysis, chemical analysis, and atomic absorption spectroscopy, mainly to detect the content of alloying elements such as aluminum, magnesium, silicon, iron, copper, and manganese.
- Mechanical Properties Testing Includes tensile testing, hardness testing, bending testing, and impact testing to evaluate the material's strength, toughness, and processability.
- Dimensional Accuracy Inspection Tools such as micrometers, thickness gauges, and calipers are used to measure parameters like thickness, width, length, fin height, and pitch.
- Surface Quality Inspection Methods such as visual inspection, roughness measurement, and cleanliness testing are used to assess surface quality, ensuring it is free of defects and contaminants.
Popular Non-Clad Aluminum Fins
Bare Aluminium Fin Stock
Bare aluminium fin stock is untreated aluminum foil with basic aluminum characteristics. Due to its untreated surface, it may be affected by oxidation and corrosion during use, but it still maintains good thermal conductivity.
Features
- Thermal Conductivity: Maintains good heat transfer performance.
- Surface Condition: The untreated surface may be affected by oxidation and corrosion.
- Application: Commonly used in heat exchangers and radiators.
Hydrophilic Aluminium Fin Stock
Hydrophilic aluminium fin stock is aluminum foil treated with a hydrophilic coating that allows condensate to spread rapidly without forming droplets.
Features
- Heat Exchange Efficiency: Increases heat exchange area and speeds up cooling and heating processes.
- Noise Reduction: Effective in reducing airflow noise due to the absence of water droplet accumulation.
- Protective Function: Provides additional corrosion and mildew protection.
- Moisture Distribution: Ensures even distribution of condensed water on the surface, reducing thermal resistance buildup and improving heat exchange rate by about 5%.

Pre-coated Aluminum Fin Stock
Pre-coated Aluminum Fin Stock features a corrosion-resistant coating that prevents corrosion, and the lubricating layer in the coating extends the service life.
- Thermal Conductivity: Provides good thermal conductivity.
- Corrosion-Resistant Coating: The coating prevents corrosion during use and extends the service life.
- Lubricating Layer: The lubricating layer in the coating improves formability and ease of processing into desired shapes and sizes.
- Application: Suitable for room/combination air conditioners and heat exchangers in large refrigerators.
Hydrophobic Aluminum Fin Stock
Hydrophobic aluminum fin stock forms a hydrophobic layer through special surface treatment, effectively reducing moisture adhesion and condensation. It is especially suitable for HVAC condensers, evaporators, and refrigeration system heat dissipation in high-humidity environments. Its hydrophobic properties reduce the likelihood of frosting and fouling, minimize cleaning and maintenance frequency, and maintain stable heat exchange efficiency, enhancing corrosion resistance and extending equipment service life.
Self-Lubricating Aluminum Fin Stock Foil
Self-lubricating aluminum fin stock foil features a lubricating layer with a low friction coefficient on the surface, which reduces friction resistance during forming and assembly processes. It facilitates operations such as bending and stacking of fins, lowers processing losses and equipment wear. This product is suitable for precision-assembly scenarios such as automotive radiators and industrial heat exchangers, ensuring the integrity and fit of the fin structure without affecting heat dissipation performance, thereby improving production efficiency and equipment stability.
Mildew-Proof Aluminum Fin Stock Foil
Mildew-proof aluminum fin stock foil is enhanced with anti-mildew ingredients or treated with antibacterial coatings to inhibit the growth of mold, bacteria, and other microorganisms on the surface. It is especially suitable for humid environments prone to mold growth, such as household air conditioners, bathroom ventilation systems, and food refrigeration equipment. Its mildew-resistant properties prevent performance degradation due to microbial growth, odor generation, and material corrosion, ensuring hygiene and safety, and extending the service cycle of the equipment.
Aluminum Fin Material Selection and Application Guide
Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Systems
Application Characteristics: Aluminum fins in air conditioning and refrigeration systems usually operate in humid environments with alternating hot and cold conditions, requiring good thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and hydrophilicity.
Material Selection:
- Base Materials: Commonly selected alloys include 1100, 3003, and 8011, known for their good thermal conductivity and formability.
- Surface Treatment: To enhance hydrophilicity and corrosion resistance, hydrophilic coating treatment is typically required. Hydrophilic coating helps condensate water form a uniform film on the fin surface, allowing quick drainage, avoiding water bridges, and improving heat transfer efficiency.
- Special Environments: For high humidity or corrosive gas environments, aluminum fins with anti-corrosion coatings or more corrosion-resistant alloys like 5052 can be selected.
Automotive Radiators and Heat Exchangers
Application Characteristics: Automotive radiators work under high temperatures, vibration, and sometimes corrosive substances, requiring excellent thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance.
Material Selection:
- Base Materials: Typically, 3003 aluminum alloy is used as the core material, and 4343 alloy as the clad layer to form a composite fin foil (4343/3003/4343 structure), which offers good brazing properties and sag resistance.
- Special Requirements: For high-temperature environments, aluminum alloys with added zirconium or titanium can be used to enhance thermal stability. For coastal or de-icing salt environments, materials with strong salt spray corrosion resistance should be considered.
- Manufacturing Process: Automotive radiator fins are usually made using brazing processes, thus requiring good brazability.
Industrial Heat Exchangers
Application Characteristics: Industrial heat exchangers operate under widely varying conditions, including temperature, pressure, and medium corrosiveness, requiring material selection tailored to specific working conditions.
Material Selection:
- General Industrial Environments: Commonly selected alloys include 3003 and 3004 aluminum-manganese alloys, which offer good corrosion resistance and workability.
- High-Temperature Environments: For high temperatures (e.g., above 300°C), aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloys such as 6061 and 6063 are suitable due to their good mechanical performance at elevated temperatures.
- Corrosive Environments: For corrosive media, choose aluminum-magnesium alloys like 5052 and 5083, or aluminum fins with anti-corrosion surface treatments.
- High-Pressure Environments: In high-pressure applications, higher-strength aluminum alloys or composite fin structures can be used to improve pressure resistance.
Architecture and Decoration Field
Application Characteristics: Aluminum fins used in architecture and decoration focus on aesthetics, weather resistance, and processability.
Material Selection:
- Base Materials: Common choices include 1100, 3003, and 5052 alloys, known for their good weather resistance and surface treatment properties.
- Surface Treatment: Based on decorative needs, surface treatments like anodizing, painting, and spraying can be applied to improve appearance and weatherability.
- Special Requirements: For high-rise buildings or coastal areas, high-strength or salt spray-resistant aluminum alloys are recommended. For fire safety applications, aluminum fins with fire-resistant coatings may be chosen.
Electronics Heat Dissipation
Application Characteristics: Aluminum fins for electronics heat dissipation require high thermal conductivity, lightweight properties, and good workability.
Material Selection:
- Base Materials: Common selections include pure aluminum like 1100 and 1060, or aluminum alloys like 3003 and 6061, which offer good thermal conductivity and formability.
- Special Requirements: For high-power electronics, higher thermal conductivity pure aluminum or copper-aluminum composite materials may be used. For electromagnetic shielding, conductive aluminum alloys are suitable.
- Manufacturing Process: Depending on heat dissipation requirements and precision needs, manufacturing methods may include extrusion, stamping, or casting.
Marine and Offshore Engineering
Application Characteristics: Aluminum fins used in marine and offshore engineering operate in high salt spray, high humidity, and possible seawater splash environments, requiring excellent corrosion resistance.
- Base Materials: Commonly selected aluminum-magnesium alloys include 5052 and 5083, known for their good seawater corrosion resistance.
- Surface Treatment: Anodizing or applying anti-corrosion coatings is typically required to further improve corrosion resistance.
- Special Requirements: For direct seawater contact, materials with anti-biofouling properties should be considered. For weldable structures, alloys with good weldability should be chosen.
Comparison Between Aluminium Fin Stock and Other Materials
Comprehensive Comparison: Aluminium Fins vs. Other Materials
| Property | Aluminium Fins | Other Materials (Copper/Stainless Steel/Steel) |
| Thermal Conductivity | (Approx. 237 W/m·K) | Copper > Aluminium > Steel > Stainless Steel |
| Density | (2.7 g/cm³, Lightweight) | Copper/Steel Heavier (Copper 8.9, Steel 7.8) |
| Cost | (Low) | Copper > Stainless Steel > Steel > Aluminium |
| Corrosion Resistance | (Requires Surface Treatment) | Stainless Steel Best, Copper Second |
| Workability | (Easy to Stamp/Bend) | Copper is Soft but Expensive; Stainless Steel/Steel Difficult to Process |
| Application Scenarios | Air Conditioning, Automotive Radiators | Special Environments (e.g., High Temperature, Severe Corrosion) |
Comparison Between Copper Fins and Aluminium Fins
| Parameter | Copper Fins | Aluminium Fins | Analysis |
| Thermal Conductivity | 398 W/m·K (Best) | 237 W/m·K | Copper conducts heat faster, suitable for high-efficiency heat dissipation |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm³ (Heavier) | 2.7 g/cm³ (Lightweight) | Aluminium reduces weight by over 50%, ideal for lightweight design |
| Cost | Expensive (about 3 times that of aluminium) | Inexpensive | Aluminium offers significant cost advantage |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (but prone to sulfide blackening) | Moderate (requires anodizing or coating) | Copper is naturally corrosion-resistant; aluminium relies on surface treatment |
| Brazing/Welding | Difficult, requires silver solder | Easy to weld (commonly brazed or glued) | Aluminium offers higher processing efficiency |
| Typical Applications | High-end electronics cooling, precision instruments | Household air conditioners, automotive condensers | Copper performs better; aluminium offers better cost-performance |
Conclusion: Copper is suitable for compact, high-efficiency heat dissipation scenarios; aluminium is the first choice for lightweight, low-cost applications.
Differences Between Stainless Steel Fins and Aluminium Fins
| Property | Stainless Steel Fin | Aluminum Fin | Key Differences |
| Corrosion Resistance | (Resistant to acid/alkali and high-temperature oxidation) | (Depends on coating) | Stainless steel excels, maintenance-free |
| Thermal Conductivity | (15–20 W/m·K, relatively poor) | (237 W/m·K) | Aluminum's conductivity is 12 times that of stainless steel |
| Mechanical Strength | (High hardness, pressure resistance) | (Soft, easily deformed) | Stainless steel suits high-pressure environments |
| Cost | (Higher, especially 316L stainless steel) | (Low cost) | Aluminum is more economical |
| Application Scenarios | Chemical equipment, offshore platforms, high-temperature furnaces | Civil refrigeration, conventional heat exchangers | Stainless steel targets extreme environments |
Aluminium Fin Stock Packaging and Storage
Packaging
- Wooden Pallets: Packaged using fumigated or non-fumigated wooden pallets.
- Wooden Cases: Fumigated or non-fumigated wooden cases can also be used for packaging, depending on the required method.
Storage
Environmental Requirements:
- Cleanliness: The storage area should be clean, free from dust and dirt.
- Dryness: Humidity should be kept below 65% to prevent the aluminum foil from moisture damage.
- Non-corrosive Gases: The storage area should be free from corrosive gases to avoid chemical corrosion of the aluminum foil.
Protective Measures:
- Rain and Snow Protection: The storage area should be protected from rain, snow, and other liquids to prevent moisture or corrosion.
- Moisture Isolation: The storage area should be free from other sources of moisture or chemically active substances to maintain the dryness and stability of the aluminum foil.
Frequently Asked Questions About Aluminum Fin Materials
Corrosion Issues and Solutions for Aluminum Fins
Pitting Corrosion
- Phenomenon: Small and deep pits appear on the material surface, usually caused by chloride ions, dust, or surface defects.
- Solution: Choose suitable aluminum alloys, perform surface treatment, clean regularly, and control environmental humidity.
Galvanic Corrosion
- Phenomenon: When aluminum fins come into contact with other metals, a potential difference leads to accelerated corrosion of the aluminum.
- Solution: Avoid direct contact with metals of significantly different potential, use insulation or separation layers, and adopt sacrificial anode protection.
Crevice Corrosion
- Phenomenon: Localized corrosion occurs in crevices, overlaps, or beneath surface deposits on aluminum fins.
- Solution: Optimize design to reduce crevices, perform sealing treatment, and apply special surface treatments to crevice-prone areas.
Deformation and Damage Handling of Aluminum Fins
Aluminum fins may experience deformation or damage during manufacturing, installation, or operation, which can affect performance and lifespan. Corresponding preventive and repair measures should be taken for issues occurring at different stages.
Causes of Performance Degradation in Aluminum Fins and Recovery Methods
Common causes of performance degradation in aluminum fins include dust and dirt accumulation, corrosion, deformation, frosting and icing, and material aging. Effective recovery methods include regular cleaning, surface repair, reshaping treatment, and performance evaluation.
