What Is Transformer Aluminum Strip?
Transformer aluminum strip is a high-purity aluminum strip specially produced for transformer windings and related electrical applications (usually with a purity above 99.5%, such as grades 1050, 1060, 1070, etc.). It is cold-rolled into specific widths, thicknesses, and mechanical properties, and is used to wind transformer coils (windings) as a conductive carrier.
Transformer aluminum strip has very high technical requirements for conductivity, burrs, edge condition, camber (side bend), and surface quality. As an important electrical material, it plays an indispensable role in power transmission and distribution systems, especially as the conductive material for high- and low-voltage windings in dry-type transformers.
During transformer operation, aluminum strip mainly undertakes the function of current transmission while participating in the electromagnetic conversion process. It is one of the core materials that affect transformer performance.
Aluminum’s electrical and thermal conductivity is second only to copper, making it one of the best conductive metals among traditional materials. Because the price of copper is much higher than that of aluminum, and with the rapid development of aluminum smelting technology, aluminum output, quality, and purity have been greatly improved. Aluminum prices have also gradually decreased, making aluminum strip an increasingly popular alternative to copper strip in transformer winding applications.
Transformer aluminum strip is favored for its excellent conductivity, light weight, good corrosion resistance, and outstanding formability. It is mainly used for manufacturing high- and low-voltage coils of dry-type and oil-immersed transformers. It is a strip-shaped conductor made from high-purity aluminum through rolling and slitting processes, which can replace copper strip to reduce cost and weight.
Among them, 1060 aluminum strip contains more than 99.6% aluminum and is one of the most commonly used grades in the aluminum strip series. Its production process is relatively simple and technologically mature, giving it a significant price advantage compared with other high-end aluminum alloys. 1350 aluminum strip is a high-purity aluminum specially designed for electrical applications, offering higher conductivity and more stable electrical performance.
When selecting, it is necessary to comprehensively evaluate:
- Initial investment cost vs. long-term operating losses (aluminum transformers may have slightly higher load losses).
- Installation space (aluminum transformers are slightly larger in size).
- The manufacturer’s technical capability (especially connection technology).
Electrical Conductivity of Transformer Aluminum Strip
- 1050: Better than 60% IACS.
- 1060: Better than 61.5% IACS.
- 1070: Better than 62.7% IACS.
- 1350: Better than 62% IACS.
Transformer Aluminium Strip Specifications
The most commonly used alloys for transformer aluminum strip belong to the 1000 series (pure aluminum) because they have the highest electrical conductivity.
| Specification | Details |
| Common Alloys | 1050, 1060, 1070, 1350 |
| Temper | O (Fully Annealed) – This makes the strip soft and easy to wind without "springing back." |
| Thickness Range | 0.1 mm to 3.5 mm (Dry-type transformers commonly use thinner strips such as 0.5–1.5 mm, while oil-immersed transformers can use thicker strips.) |
| Width Range | 10 mm to 1600 mm |
| Conductivity | ≥ 61% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) |
| Surface Quality | Clean, free of oil, uniformly oxidized, no scratches or burrs |
| Edge Treatment | Usually rounded edges (chamfered) to prevent puncturing the interlayer insulation during winding |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Thickness tolerance ≤ ±0.01 mm, width tolerance ≤ ±0.1 mm |
| Delivery Form | Coil or strip, factory direct supply |

Transformer Aluminum Strip Materials & Grades
Transformer aluminum strip mainly uses 1xxx series pure aluminum, featuring high aluminum content and excellent electrical conductivity. Common grades and their characteristics are as follows:
| Grade | Aluminum Content | Conductivity | Features | Typical Applications |
| 1050 (O) | 99.50% | Good | Moderate cost, well-balanced performance | Distribution transformers, general-purpose |
| 1060 (O) | 99.60% | Excellent | Slightly higher conductivity than 1050 | Dry-type transformers, 35kV class |
| 1070 (O) | 99.70% | Very High | High purity, low resistivity | High-performance transformers, reactors |
| 1350 (O) | 99.50%+ | Ultra High | Electrical-grade pure aluminum, conductivity close to 62% of copper | Large power transformers |
Temper: Almost all are supplied in O temper (soft annealed). After full annealing, the strip offers excellent winding performance and elongation, preventing cracking during coil winding.
Transformer Aluminum Strip Surface Treatment
To improve the insulation performance and corrosion resistance of transformer aluminum strips, special surface treatments are often required:
Insulation Coating Treatment
A layer of insulating material, such as polyester or polyimide, is applied to the aluminum strip surface to enhance interlayer insulation performance.
Passivation Treatment
A passivation film is formed on the aluminum strip surface through chemical treatment to enhance corrosion resistance.
Anti-Oxidation Treatment
A special anti-oxidation layer is formed on the surface of the aluminum strip to prevent oxidation during long-term use.
Anti-Sticking Treatment
Special treatment is performed on the surface of the aluminum strip to prevent sticking during the winding process.
These surface treatment processes can be selected according to specific usage environments and requirements to ensure that transformer aluminum strips can operate reliably under various working conditions.
Transformer Aluminum Strip Quality Requirements
As a professional transformer aluminum strip manufacturer, Haomei Aluminum fully understands that aluminum strip for transformers is fundamentally different from ordinary industrial aluminum strip in terms of performance and safety. To meet the long-term stable operation requirements of power equipment, we implement much stricter technical standards in production and quality inspection, ensuring every coil meets transformer-grade application requirements:
High-Precision Burr-Free Edge Control
Using precision slitting and online inspection processes, we ensure smooth, rounded and chamfered edges with no micro burrs, preventing damage to insulation paper or films during winding and reducing the risk of short circuits and equipment failure from the source.
Excellent Surface Quality
The aluminum strip surface is kept extremely clean and smooth, free from oil stains, scratches, dents, or oxidation defects, ensuring uniform contact and stable insulation performance to meet the strict reliability requirements of transformers.
Strict Control of Camber and Flatness
Through tension control and leveling processes, side camber is minimized so that the strip can be tightly and straightly wound onto the core, improving winding stability and overall transformer performance.
Relying on mature production experience and a complete quality management system, Haomei Aluminum continuously provides stable and reliable transformer aluminum strip solutions, helping power equipment achieve higher safety and operating efficiency.

Transformer Aluminum Strip Features
As a key conductive material for transformer windings, the quality of aluminum strip directly affects the performance and reliability of the entire transformer. We select high-purity aluminum and apply precision processing to ensure every coil consistently meets the stringent requirements of power equipment.
Stable and Reliable Electrical Conductivity
Conductivity reaches 60%–62% of copper, achieving an excellent balance between performance and cost. High-purity raw material ensures consistent resistivity, reduces energy loss, and improves overall transformer efficiency.
Strict Surface and Dimensional Control
From rolling to slitting, the entire process is tightly controlled. The strip is clean and flat, free of oil, scratches, and oxidation spots, with precise thickness and width tolerances to ensure consistent winding resistance and structure, making winding smoother and finished products more stable.
Burr-Free Rounded Edges for Higher Safety
Using special precision cutting and edge rounding processes, the edges are smooth and burr-free, preventing insulation damage during winding and greatly reducing the risk of short circuits, improving long-term safety and reliability.
Flexible and Durable for Complex Winding Structures
Fully annealed (O temper) aluminum strip offers excellent elongation (≥25%), is not easy to crack or break during winding, and easily adapts to multi-layer, multi-angle, and special-shaped coil structures, improving production efficiency and yield.
Good Heat Dissipation, Corrosion Resistance, Longer Service Life
Excellent thermal conductivity helps reduce operating temperature, while aluminum’s natural corrosion resistance ensures stable performance even in long-term service environments.
Lightweight with Clear Cost Advantages
Under the same conductivity requirement, aluminum’s density is only about 30% of copper, helping reduce transformer weight by more than 40%. At the same time, material cost is only about 1/3–1/4 of copper, providing a highly competitive overall cost advantage for transformer manufacturers.
Technical Advantages of Aluminum Strip for Transformer Windings
Excellent Electrical Conductivity
Aluminum’s conductivity is only behind silver, copper, and gold, ranking fourth among commonly used metals. While aluminum has a conductivity of about 37.7×10^6 S/m, compared to copper's 58×10^6 S/m, it is sufficient to meet the needs of most transformers.
Through proper design of the aluminum strip’s cross-sectional area and winding structure, aluminum-wound transformers can achieve electrical performance comparable to copper-wound transformers. For transformers, performance depends not only on materials, but also significantly on structural design and manufacturing technology.
Good Thermal Conductivity
Transformers generate heat during operation. Good thermal conductivity is another key feature of transformer aluminum strips. Aluminum's thermal conductivity is 237 W/(m·K), lower than copper’s 397 W/(m·K), but significantly higher than other common metals.
This good thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat during transformer operation, keeping it within normal operating temperatures, and improving reliability and lifespan. Especially under high-load and high-temperature conditions, aluminum strips help reduce hot spot temperatures and slow insulation aging.
Significant Weight Reduction Advantage
Aluminum has a density of about 2.7 g/cm³, much lower than copper's 8.96 g/cm³, giving aluminum-wound transformers a significant weight advantage. For the same capacity, aluminum-wound transformers are typically 30%-40% lighter than copper-wound ones.
This lightweight feature brings multiple benefits: lower transportation costs, easier installation, reduced structural load, and easier maintenance—ideal for weight-sensitive applications like high-rise buildings and mobile substations.
Obvious Cost Advantage
Aluminum’s price is significantly lower than copper’s, giving aluminum-wound transformers a clear cost advantage. Market data shows that aluminum typically costs about one-third as much as copper.
This cost benefit applies not only to material procurement but also to overall transformer manufacturing: lower density means less material is needed for the same electrical performance; good workability lowers processing costs; abundant aluminum resources make prices more stable.
Good Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum quickly forms a dense aluminum oxide film in air, effectively preventing further oxidation and corrosion. In most natural and general industrial environments, aluminum windings have good corrosion resistance.
In contrast, copper may corrode in specific environments (e.g., those with sulfides or chlorides). Therefore, aluminum-wound transformers may offer better long-term reliability in certain conditions.
Excellent Workability
Transformer aluminum strips are usually supplied in the O temper (soft), offering excellent ductility and processability. This condition allows easy bending, winding, and forming to meet complex winding structure needs.
Specifically, the processing advantages of transformer aluminum strip include: good elongation and tensile strength, meeting standard processing requirements (stamping, stretching); high formability for various shapes; weldability via gas welding, atomic hydrogen welding, and contact welding; and good capability to withstand pressure processing and bending.

Aluminum Strips for Transformers Chemical Composition
1050 O Aluminum Strips Chemical Composition
| Element | Al | Si | Fe | Mg | Zn | Mn | Ti | Cu | V |
| Standard Value | ≥99.5 | 0.0431 | 0.203 | 0.0013 | 0.0093 | 0.0104 | 0.02 | 0.0022 | 0.0039 |
1060 O Aluminum Strips Chemical Composition
| Element | Al | Si | Fe | Mg | Zn | Mn | Ti | Cu | V |
| Standard Value | ≥99.6 | 0.0431 | 0.203 | 0.0013 | 0.0093 | 0.0104 | 0.02 | 0.0022 | 0.0039 |
1070 O Aluminum Strips Chemical Composition
| Element | Al | Si | Fe | Mg | Zn | Mn | Ti | Cu | V |
| Standard Value | ≥99.7 | 0.0431 | 0.203 | 0.0013 | 0.0093 | 0.0104 | 0.02 | 0.0022 | 0.0039 |
1350 O Aluminum Strips Chemical Composition
| Element | Al | Si | Fe | Mg | Zn | Mn | Ti | Cu | V |
| Standard Value | ≥99.5 | 0.0431 | 0.203 | 0.0013 | 0.0093 | 0.0104 | 0.02 | 0.0022 | 0.0039 |
Transformer Aluminum Strip Thickness Tolerance
| Thickness | Thickness Tolerance |
| 0.1-0.2 | +/-8% |
| 0.2-0.4 | +/-0.02 |
| 0.4-0.8 | +/-0.03 |
| 0.8-1.1 | +/-0.04 |
| 1.1-1.4 | +/-0.05 |
| 1.4-2.0 | +/-0.06 |
| 2.0-2.5 | +/-0.07 |
| 2.5-3.0 | +/-0.08 |
Transformer Aluminum Strip Width tolerance
| Thickness(mm) | Width tolerance(%) | ||||
| <100 | 100-300 | 300-500 | 500-1250 | 1250-1500 | |
| >0.1-0.20 | +/-0.15 | +/-0.2 | +/-0.3 | +/-0.5 | +/-0.5 +/-1 |
| 0.20-0.60 | +/-0.15 | +/-0.2 | +/-0.3 | +/-0.75 | +/-0.5 +/-1.25 |
| 0.60-1.0 | +/-0.15 | +/-0.25 | +/-0.5 | +/-0.75 | +/-0.5 +/-1.25 |
| 1.0-2.0 | +/-0.2 | +/-0.35 | +/-0.6 | +/-1 | +/-0.5 +/-1.25 |
| 2.0-3.0 | +/-0.5 | +/-0.5 | +/-0.75 | +/-1 | +/-0.5 +/-1.25 |
Transformer Aluminum Strip Burrs and collapse
| The width of aluminium strip (mm) | Burr’s height (mm) | Collapsed side’s height (mm) |
| <0.2 | 0.01 | ≥0.05-0.1 |
| 0.2-1.0 | 0.015 | |
| 1.1-1.5 | 0.02 | |
| >1.6 | 0.03 |
Types of Aluminum Strips for Transformers
Transformer Aluminum Strip 1050 O
The 1050 aluminum foil strip contains 99.5% aluminum, offering excellent conductivity and flexibility. It is fully annealed in the O temper, making the foil softer and easier to process. It is commonly used in transformer windings and is suitable for applications requiring high conductivity and good ductility.
The 1050 O aluminum strip is one of the most commonly used materials in transformers. It is frequently used as support material in transformer windings, which helps to reduce transformer losses and improve performance.
The thickness of the 1050 O aluminum strip used in transformers generally ranges from 0.1mm to 1mm. It is available in single or double-layer structures, which can effectively reduce magnetic leakage in coils and enhance insulation performance.
Transformer Aluminum Strip 1060 O
The 1060 aluminum foil strip has an aluminum content of up to 99.6%, offering excellent electrical conductivity and high corrosion resistance. In the O temper, 1060 aluminum foil is softer and easier to shape, making it suitable for winding transformer coils, especially where strict electrical and mechanical performance is required.
1060 O aluminum alloy has good plasticity but lower strength compared to other alloys. It is mainly used in various high and low voltage electrical devices, such as transformer windings.
Transformer Aluminum Strip 1070 O
The 1070 aluminum foil strip is based on high-purity aluminum with 99.7% aluminum content. It has outstanding conductivity and good flexibility and durability. The 1070 O temper foil can form stable coil structures during transformer winding, making it suitable for transformer designs that require higher conductivity and ductility.
The 1070 O aluminum foil for transformer windings can be used in dry-type transformers, oil-immersed transformers, and reactor windings.
The 1070 O aluminum foil for transformer windings has excellent heat dissipation properties, and does not increase the temperature rise of the coil during long-term operation, thus extending the coil's service life. Using 1070 O aluminum foil for transformer windings can reduce the cost of batch manufacturing transformers by 15%.
Transformer Aluminum Strip 1350 O
The 1350 aluminum foil strip is a high-purity aluminum foil with an aluminum content exceeding 99.5%, widely used in transformer windings. The 1350 O temper foil, after annealing, has excellent plasticity and flexibility, meeting the high conductivity and mechanical stability requirements for transformer winding materials.
The 1350 O aluminum foil for transformer windings is widely used in the transformer industry, including oil-immersed transformers and dry-type transformers.
The 1350 O aluminum foil for transformer windings is available in both bare and coated types. The bare type is mainly used as winding material for oil-immersed transformers, while the coated type is primarily used as interlayer insulation material.
Transformer Aluminum Strip Winding Structure & Design
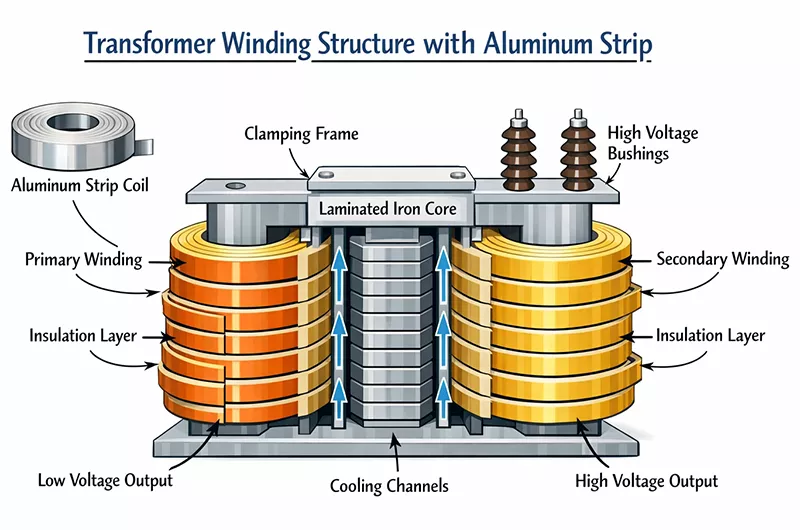
Aluminum Strip Coil
- Rolled from high-purity aluminum with a flat strip cross-section
- Continuously wound into coils during the manufacturing process
- Compared with round wire, aluminum strip offers a higher filling factor, better heat dissipation, and more uniform mechanical strength
Primary Winding
- The input winding located on one side of the iron core, usually connected to the power grid
- Formed by multi-layer winding of aluminum strips
- Relatively fewer turns with larger current
- Responsible for converting input electrical energy into magnetic energy
Secondary Winding
- The output winding located on the other side of the iron core, supplying power to the load
- Also wound using aluminum strips
- The number of turns is designed according to the transformation ratio and is usually greater than that of the primary winding
- Outputs high voltage or low voltage (depending on the design)
Insulation Layer
- A critical structure positioned between each layer of aluminum strip
- Common materials: electrical insulation paper, insulating films, and composite insulation materials
- Prevents interlayer short circuits
- Also helps form oil ducts or air ducts to improve heat dissipation
Laminated Iron Core
- The magnetic circuit core of the transformer
- Laminated from silicon steel sheets to reduce eddy current losses
- Provides a closed magnetic flux path for the primary and secondary windings
- Determines the transformer’s efficiency and no-load losses
Cooling Channels
- Heat dissipation channels reserved between the windings and the iron core, as well as within the windings
- Facilitate the circulation of transformer oil or air
- Reduce operating temperature rise of the windings
- Especially important for aluminum strip windings (high-current, low-loss designs)
Clamping Frame
- Used to mechanically secure the iron core and windings
- Prevents winding deformation during transportation or short-circuit impacts
- Enhances overall mechanical strength
- Reduces operating noise
High Voltage Bushings
- High-voltage terminals of the transformer
- Provide electrical insulation and mechanical support
- Safely conduct electrical energy from the windings to external circuits
- Commonly used in oil-immersed and dry-type transformers
Low Voltage Output / High Voltage Output
- Low Voltage Output: low-voltage side output with high current
- High Voltage Output: high-voltage side output with high voltage
Transformer Aluminum Strip Applications
Dry-type Transformer Winding
Transformer aluminum strip is widely used in low-voltage windings of dry-type transformers. As a high-performance aluminum strip for transformers, it features stable electrical conductivity, excellent formability, and corrosion resistance, ensuring long-term safe operation of the windings. It is a proven and mature choice for power equipment manufacturers.
Oil-immersed Distribution Transformer
In medium- and low-voltage windings, aluminum winding strip has become one of the mainstream conductor materials. Compared with copper, electrical aluminum strip significantly reduces cost while maintaining electrical performance, making it an ideal solution for high cost-performance distribution transformer design.
Substation & Reactor
High-quality transformer aluminum strip is suitable for windings in substations and reactors, providing uniform conductivity and good thermal stability, improving overall reliability and service life of power equipment.
Renewable Energy
In photovoltaic inverters and wind power transformers, aluminum strip for transformers is widely applied. Its lightweight and high-efficiency conductivity advantages help improve energy conversion efficiency and reduce overall system cost.
High-frequency Transformer
Some high-frequency electronic transformers use aluminum winding strip to replace copper strip. While meeting high-frequency electrical performance requirements, it achieves lightweight design and cost optimization, especially suitable for electronic power supplies and renewable energy power systems.
Distribution Transformer
Whether pole-mounted transformers or box-type distribution transformers, electrical aluminum strip is one of the standard winding materials, providing stable and reliable power transmission for the grid.
Renewable Power Grid
In inverters and step-up transformers for solar and wind grid-connection systems, transformer aluminum strip helps improve overall system reliability and service life thanks to its good conductivity and durability.
Main Material for Large Transformer Coils
Aluminium strips are primarily used for winding transformer coils, helping to improve the efficiency and reliability of transformers. Their properties make them suitable for various types of transformers, including distribution transformers and power transformers.
- Dry-Type Transformers: Due to their light weight and corrosion resistance, aluminium strips are the preferred choice for windings.
- Oil-Immersed Transformers: The usage rate is continuously increasing, as they save costs and reduce maintenance.
- Distribution: Used in transformers up to 4 MVA.
Applications in Solar and Power Industry
Aluminium strips, as conductive materials for the high and low-voltage windings of dry-type transformers, are suitable for use in the power industry, solar energy, and other fields.
Other Industries that Use Transformer Aluminium Strips
| Industry | Description |
| Industrial Automation | Transformer aluminium strips are used in power and control transformers for automation equipment, helping to ensure stable operation of equipment under high loads. |
| Transportation Industry | In fields like railways, subways, and electric vehicles, aluminium strips are used in power transformers and electric vehicle charging equipment to achieve efficient power transmission. |
| Renewable Energy | In addition to solar energy, aluminium strips are also used in wind power generation facilities, especially in wind power transformers, utilizing aluminium’s conductivity and lightweight advantages to enhance efficiency. |
| Marine and Offshore Engineering | In ship power systems, aluminium strips are used as transformer winding materials. They can withstand the corrosion of seawater, offering good corrosion resistance and ensuring long-term reliability in harsh environments. |
| Household Appliances | Aluminium strips are used in transformers and motor winding materials in home appliances, helping to reduce production costs and improve energy efficiency and reliability. |
| Data Centers and Communication Facilities | Transformer aluminium strips are widely used in data centers, communication stations, and other facilities in power transformers, ensuring efficient and stable operation, especially in environments that require large amounts of power. |
Transformer Aluminum Strip Customer Application Cases
Dry-Type Transformer Applications
Dry-type transformers are the main application area for aluminum strip windings, especially in places with high fire protection, explosion-proof, and environmental requirements. Aluminum strip for dry-type transformers features high conductivity, softness, smooth surface, and no burrs, making it an ideal material.
Power Transformer Applications
Aluminum strip wound transformers are also widely used in power systems, especially in medium and low voltage distribution transformers. Compared to traditional copper-wound transformers, aluminum-wound ones offer high efficiency, low losses, energy savings, compact size, light weight, strong overload capacity, and safe and reliable operation.
Special Environment Applications
Aluminum strip wound transformers perform well in special environments: humid conditions, high temperatures, corrosive environments, mobile and portable applications.
New Energy Applications
Aluminum strip wound transformers also have broad application prospects in new energy fields such as wind power, solar power, and energy storage systems.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Transformer Aluminum Strip
Advantages of Transformer Aluminum Strip
Aluminum naturally forms a dense oxide film on its surface, giving it good corrosion resistance, low cost, and light weight.
Disadvantages of Transformer Aluminum Strip
- Lower conductivity: Aluminum’s electrical conductivity is about 61% of copper. To achieve the same current-carrying capacity, the cross-sectional area of an aluminum conductor needs to be about 1.6 times that of copper, resulting in larger coil size.
- Difficult welding/connection: The oxide film on aluminum has a high melting point, so welding requires special techniques and equipment (such as ultrasonic welding and TIG welding). Improper joint treatment can easily lead to increased contact resistance and overheating.
- Lower mechanical strength: Aluminum is softer than copper, and its ability to withstand electrodynamic force caused by short-circuit current is weaker, requiring reinforced structural design.
- Higher thermal expansion coefficient: Aluminum expands and contracts more with temperature changes, which may affect long-term operational stability.
Comparison Between Aluminum Strip Transformers and Copper Winding Transformers
Although copper is a better conductor, aluminum has significant advantages in logistics and economics.
- Cost: Aluminum is about 30–50% cheaper than copper, and its price is usually more stable in the global market.
- Weight: Aluminum density (2.7 g/cm³) is about one third of copper (8.96 g/cm³). Although aluminum windings require a larger cross-sectional area to carry the same current, the final transformer is still much lighter.
- Thermal performance: Aluminum strip dissipates heat more evenly than round copper wire, reducing “hot spots” that cause insulation aging.
- Space: The main drawback is that, at the same current, aluminum requires about 66% more cross-sectional area than copper, resulting in a larger overall transformer size.
| Feature | Aluminum Strip Transformer | Copper Strip/Wire Transformer |
| Cost | Low (significant material cost advantage) | High |
| Weight | Light (about 30%–40% lighter) | Heavy |
| Size | Larger (for the same capacity) | Compact |
| Conductivity | Lower (requires larger cross-sectional area) | Excellent |
| Connection Reliability | High requirements, complex process | Easy, mature process |
| Short-circuit Withstand Ability | Requires reinforced design | Inherent advantage |
| Long-term Temperature Rise | Can meet standards with proper design | Usually lower |
| Main Market | Cost-sensitive distribution transformers, dry-type transformers | Medium & large power transformers, high-reliability applications |
Why use aluminum strip instead of traditional copper wire/copper strip?
The core driving forces are cost and weight:
- Significant cost advantage: The price of aluminum is much lower than copper (about one third of copper), which can greatly reduce raw material cost in mass-produced transformers.
- Lightweight: The density of aluminum is about one third of copper, making the transformer much lighter and easier for transportation and installation.
- Resource and strategic considerations: Aluminum resources are relatively abundant, and using aluminum helps reduce dependence on copper resources.
Working Principle of Transformer Aluminum Strip
Transformer aluminum strip primarily utilizes the electrical conductivity of aluminum to form a current path in the transformer. When alternating current passes through the aluminum strip, it generates an alternating magnetic field, achieving energy conversion and transmission through electromagnetic induction. Compared with traditional copper strip, aluminum strip offers lower cost and lighter weight while maintaining good electrical conductivity. The working principle of transformer aluminum strip is based on the use of aluminum’s conductivity to form a current path. When alternating current flows through the aluminum strip, it creates an alternating magnetic field that enables power conversion and transmission via electromagnetic induction. Compared to copper strip, aluminum strip offers reduced cost and weight with good conductivity.
Transformer Aluminum Strip Selection Guide
Key Points for Selecting and Using Transformer Aluminum Strip
- Material selection: Choose the appropriate grade according to transformer capacity and voltage class (1060 for medium and high voltage, 1050 for low voltage).
- Temper confirmation: Must be O temper; avoid using H temper (half-hard / hard), which will affect winding performance.
- Surface quality: Check that the surface is free from scratches and burrs, with uniform chamfered edges.
- Dimensional accuracy: Strictly control thickness tolerance, as it directly affects coil resistance and loss.
- Connection process: Use ultrasonic welding or special aluminum-copper transition connectors to avoid excessive contact resistance.
With its outstanding cost-performance ratio and lightweight advantages, transformer aluminum strip has become the mainstream choice in modern transformer manufacturing, especially for dry-type transformers. Through proper design (increasing cross-sectional area to compensate for lower conductivity) and process optimization, aluminum strip transformers can fully meet the performance requirements of power systems and are an ideal solution for saving energy and reducing costs.
Select Aluminum Alloy Grade Based on Transformer Type
Choosing the correct alloy ensures stable conductivity and mechanical performance during winding.
Common alloys for transformer aluminum strip:
1060 / 1070 Aluminum
Widely used in distribution transformers due to high electrical conductivity and excellent formability.
1350 Electrical Grade Aluminum
Specifically designed for electrical conductors. Offers consistent conductivity and low resistivity, ideal for large current windings.
Different types of transformers have varying performance requirements for aluminum strips. The appropriate alloy grade should be selected according to the specific application scenario:
Dry-Type Transformers
Typically, 1060 or 1070 grade aluminum strips are selected. These materials have high purity and good electrical conductivity, meeting the performance requirements of dry-type transformers.
Oil-Immersed Transformers
1050 or 1060 grade aluminum strips can be used. These materials have good corrosion resistance and workability, making them suitable for use in oil-immersed environments.
Special Transformers
For example, high-frequency transformers and pulse transformers may require specialized electrical aluminum strips such as 1350, which offer higher conductivity and more stable electrical performance.
Selection tip:
For transformer windings, electrical conductivity should always be prioritized over strength. Alloys with higher purity deliver lower losses and better energy efficiency.
Select Specifications Based on Technical Parameters
When selecting transformer aluminum strips, the specifications should be chosen based on specific technical parameter requirements:
- Thickness selection: The thickness of the aluminum strip should be determined based on the transformer's rated capacity, operating voltage, and winding structure. Generally, the larger the capacity and higher the voltage, the thicker the aluminum strip required.
- Width selection: The width of the aluminum strip should be based on winding design requirements and winding processes, while also considering the capacity of winding equipment.
- Conductivity requirements: Select aluminum strips with appropriate conductivity based on the transformer's efficiency requirements and loss limitations. Generally, the higher the conductivity, the lower the winding loss—but the higher the cost.
- Mechanical performance requirements: Choose aluminum strips with appropriate tensile strength and elongation based on the winding process and structure to ensure no breakage or excessive deformation occurs during winding.
Cost-Performance Analysis and Long-Term Cost Consideration
When selecting transformer aluminum strips, one should not only consider the initial purchase cost, but also conduct a comprehensive cost-performance analysis and long-term cost evaluation:
Cost Factor Analysis
- Initial cost: Compare quotations from different suppliers, including material cost, processing cost, and transportation cost.
- Operating cost: Consider the impact of aluminum strip conductivity on transformer losses and calculate the energy consumption cost during long-term operation.
- Maintenance cost: Consider how the quality of aluminum strips affects transformer maintenance frequency and cost.
- Service life: Evaluate how the quality and performance of aluminum strips affect transformer lifespan, and calculate the total lifecycle cost.
- Reliability value: Consider the potential value brought by the improved reliability and safety of the transformer due to high-quality aluminum strips.
By comprehensively considering these factors, one can choose the most cost-effective transformer aluminum strip product to achieve long-term economic and technical benefits.
Transformer Aluminum Strip Production Process
Raw Material Preparation
Select aluminum ingots with appropriate purity, perform accurate ingredient calculation, and carry out impurity removal and preheating treatment to ensure impurity content ≤0.02%. High-quality raw materials are the foundation for producing high-quality transformer aluminum strips.
Melting and Refining
Add pretreated aluminum ingots and alloying elements into the melting furnace and heat to 700–800℃ for melting. Stir uniformly for 30–45 minutes. Use gas blowing and filtration to remove impurities and gases, and precisely control the molten aluminum temperature to prepare for subsequent casting.
Casting and Ingot Treatment
Pour the molten aluminum into molds to form ingots, control the cooling rate to avoid internal stress and defects, and perform homogenization treatment to improve internal structure and ensure uniform grain structure.
Rolling and Heat Treatment
Heat the ingot to 550–580℃ for hot rolling. Further reduce thickness through cold rolling to the target thickness. Perform final annealing on the cold-rolled aluminum strip to obtain the desired O temper (soft condition), improving flatness and surface quality.
Finishing and Surface Treatment
Slit the aluminum strip to the required width, chamfer and deburr the edges, clean the surface to remove oil and impurities, and perform surface treatments such as passivation or coating as needed to enhance corrosion resistance and insulation performance.
Quality Control and Inspection
Conduct comprehensive quality inspections on incoming raw materials, key process parameters during production, and finished products. Tests include chemical composition analysis, conductivity testing, mechanical property testing, dimensional measurement, and visual inspection. Establish a complete quality traceability system.
Processing and Treatment of Transformer Aluminium Strips
Processing of Transformer Aluminium Strips
- Raw Material Preparation and Heating: First, the aluminium ingots are placed in a furnace and heated. The furnace temperature gradually increases to an appropriate range to melt the aluminium. Alloying elements are added during the melting process to remove impurities and enhance the purity and performance of the aluminium.
- Casting and Billet Cutting: After impurities are removed from the molten aluminium, it is cast into aluminium billets, which are then cut into aluminium plates of the specified thickness for further rolling processes.
- Rough Rolling: The cut thick plates are sent to the cold rolling machine for rough rolling. The cold rolling process gradually reduces the thickness of the aluminium plates and initially adjusts the material’s mechanical properties to meet the requirements for the subsequent hot rolling.
- Hot Rolling and Finishing: The rough-rolled aluminium plates are sent to the hot rolling mill for further processing. The hot rolling process, conducted at higher temperatures, effectively enhances the ductility and toughness of the aluminium strips, resulting in finished strips that meet the specifications.
- Annealing: After rolling, the aluminium strips undergo an annealing process. Annealing involves heating the material to a certain temperature and maintaining it for a period to relieve internal stresses, improve ductility, flexibility, and corrosion resistance, ensuring the stability of the aluminium strip’s performance.
- Cutting and Shaping: The edges of the annealed aluminium strips are trimmed to ensure accurate dimensions and smooth edges.
- Packaging and Shipping: Finally, the finished transformer aluminium strips undergo quality inspection and are coiled and packaged according to customer requirements. Once the packaging is complete, the aluminium strips are safely transported to the designated location for use.
Manufacturing Considerations
When selecting aluminium strips for transformer windings, factors such as alloy grade, thickness, width, and edge treatment must be considered to meet the specific transformer design requirements. Proper annealing and surface treatment can further improve performance and extend service life.
Transformer aluminium strips offer a combination of electrical efficiency, mechanical strength, and economic feasibility, making them the preferred material for transformer manufacturing.
